 |
SG++-Doxygen-Documentation
|
 |
SG++-Doxygen-Documentation
|
Basic algorithm for getting all affected basis functions. More...
#include <AlgorithmEvaluation.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| AlgorithmEvaluation (GridStorage &storage) | |
| double | operator() (BASIS &basis, const DataVector &point, const DataVector &alpha) |
| Returns evaluations of all basis functions that are non-zero at a given evaluation point. More... | |
| ~AlgorithmEvaluation () | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | rec (BASIS &basis, const DataVector &point, size_t current_dim, double value, GridStorage::grid_iterator &working, index_t *source, const DataVector &alpha, double &result) |
| Recursive traversal of the "tree" of basis functions for evaluation, used in operator(). More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| GridStorage & | storage |
Basic algorithm for getting all affected basis functions.
This implicitly assumes a tensor-product approach and local support. No grid points on the border are supported.
The main idea behind this algorithm is to spend as few function evaluations as possible. Assume a regular sparse grid level 3 in two dimensions with the sparse grid basis \(\Phi:=\{\phi_i(x), i=1,\ldots,N\}\). Then the tableau of subspaces looks as follows:
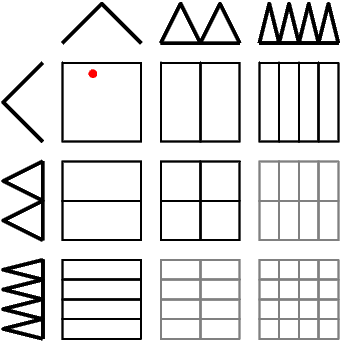
You could evaluate the function \( f_N(x) = \sum_{i=1}^N \alpha_i \phi_i(x)\) for all basis functions \(\phi_i(x)\), multiply them with the surplus and add them up. In \(d\) dimensions this would lead to \(N\) evaluations of \(d\) one-dimensional basis functions each.
A better way is to (recursively) look at each subspace, as only one basis function per subspace can be non-zero (partially disjunct supports):
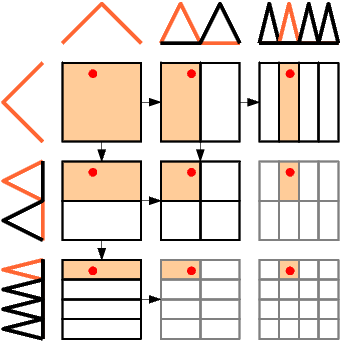
This can be done recursively in both the dimension and the level. In each subspace the basis function concerned can be identified via a few index calculations and evaluated at the given point in the domain.
Even better would be to save further function evaluations and to reuse intermediate values obtained by the evaluation of one-dimensional basis functions, see the following figure.
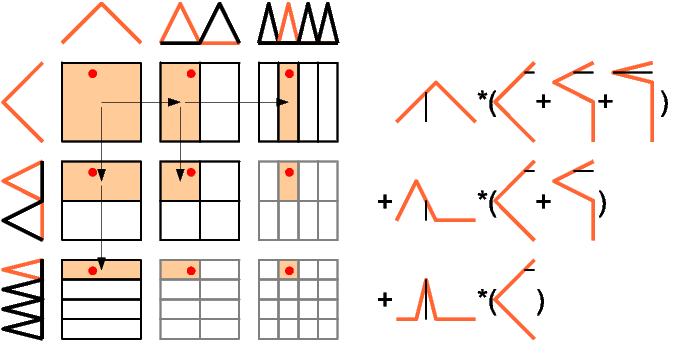
Descending recursively in the d-th dimension, one can propagate the value of the intermediate function evaluation for the first d-1 dimensions that have already been looked at.
|
inlineexplicit |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Returns evaluations of all basis functions that are non-zero at a given evaluation point.
For a given evaluation point \(x\), it stores tuples (std::pair) of \((i,\phi_i(x))\) in the result vector for all basis functions that are non-zero. If one wants to evaluate \(f_N(x)\), one only has to compute
\[ \sum_{r\in\mathbf{result}} \alpha[r\rightarrow\mathbf{first}] \cdot r\rightarrow\mathbf{second}. \]
| basis | a sparse grid basis |
| point | evaluation point within the domain |
| alpha | the sparse grid's coefficients |
References chess::dim, sgpp::base::HashGridStorage::getBoundingBox(), sgpp::base::HashGridStorage::getDimension(), sgpp::base::BoundingBox::isContainingPoint(), sgpp::base::AlgorithmEvaluation< BASIS >::rec(), sgpp::base::AlgorithmEvaluation< BASIS >::storage, and sgpp::base::BoundingBox::transformPointToUnitCube().
|
inlineprotected |
Recursive traversal of the "tree" of basis functions for evaluation, used in operator().
For a given evaluation point \(x\), it stores tuples (std::pair) of \((i,\phi_i(x))\) in the result vector for all basis functions that are non-zero.
| basis | a sparse grid basis |
| point | evaluation point within the domain |
| current_dim | the dimension currently looked at (recursion parameter) |
| value | the value of the evaluation of the current basis function up to (excluding) dimension current_dim (product of the evaluations of the one-dimensional ones) |
| working | iterator working on the GridStorage of the basis |
| source | array of indices for each dimension (identifying the indices of the current grid point) |
| alpha | the spars grid's ansatzfunctions coefficients |
| result | reference to a double into which the result should be stored |
References sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::get(), sgpp::base::HashGridStorage::getDimension(), sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::hint(), sgpp::base::HashGridStorage::isInvalidSequenceNumber(), sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::leftChild(), sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::resetToLevelOne(), sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::rightChild(), and sgpp::base::HashGridIterator::seq().
Referenced by sgpp::base::AlgorithmEvaluation< BASIS >::operator()().
|
protected |
Referenced by sgpp::base::AlgorithmEvaluation< BASIS >::operator()().